Factor out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), 'dy' dy(x 2 1y 2) = 0 Factor a difference between two squares dy((x y)(x 1y)) = 0 Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'dy' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying dy = 0 Solving dy = 0 Move all terms containing d to Explanation d dx (y x) = eyx Making z = x y → z' = 1 y' then y' 1 = exy → z' = ez or dz ez = dx or e−zdz = dx and integrating both sides −e−z = x C0 or y = − (ln(C1 − x) xTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `x(1y^2)dxy(1x^2) dy=0`

Differential Equations Solved Examples 17
(e^x y)dx (2 x ye^y)dy=0 y(0)=1
(e^x y)dx (2 x ye^y)dy=0 y(0)=1- Solve the linear differential equation (y e^sin^1 x)(dx/dy) √(1 x2) = 0 asked in Ordinary Differential Equations by Anjali01 (Answer to Solve the given initial value problems a) (e^xy) \\,dx (2xye^y)\\,dy = 0;
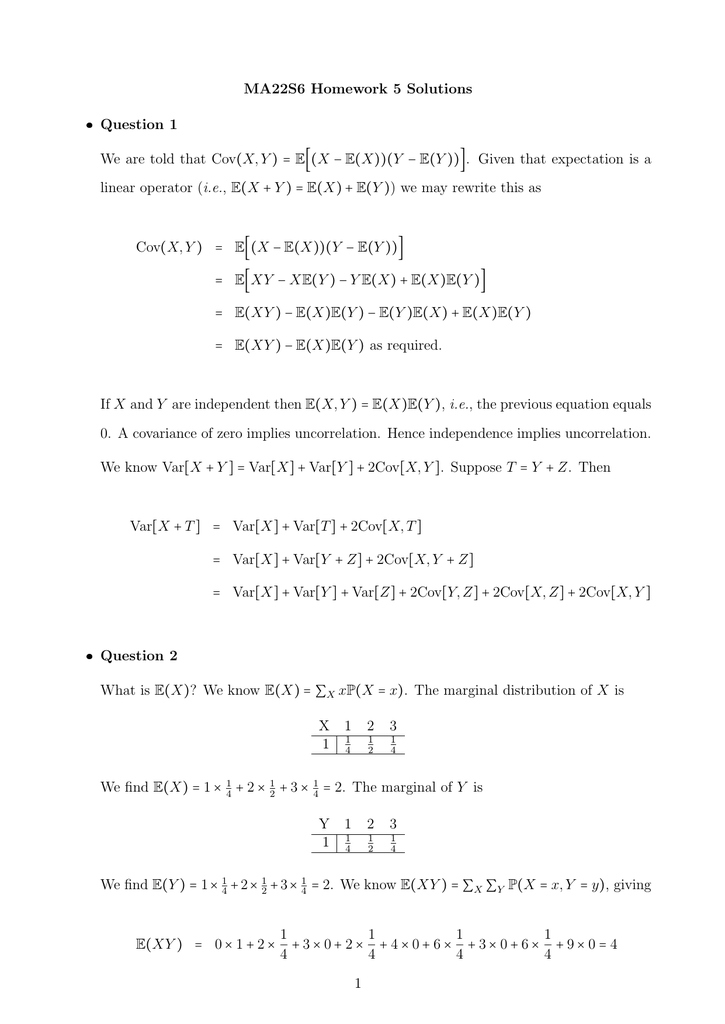



Ma22s6 Homework 5 Solutions ˆ Question 1
1 Multiple by xayb so Mdx Ndy = 0 with M = xayb 1 xa 1yb 2, N = xa 1yb xa 2yb 1 xa 3yb 2 We choose a, b to achieve 0 = ∂yM − ∂xN = (b 1)xayb (b 2)xa 1yb 1 − (a 1)xayb − (a 2)xa 1yb 1 − (a 3)xa 2yb 2 = xayb((b − a)(1 xy) − (a 3)(xy)2) a = b = − 3 So 0 = Mdx Ndy = (x −The equation is exact because (e^y ye^x)_y = (xe^y e^x)_x = e^y e^x Then is the total differential dF(x,y) =0 solved by F_x = e^y ye^x F_y = xe^y e^x Integrating this Eq leads to F(x,y) = xe^yye^x G(x) The function G(x) is obtainedSimple and best practice solution for y(xy1)dx(x2y)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it
\\quad y(0)=1 b) (y^2\\cos x 3x^2y2x)\\,dx (2y\\sin5 (e y1)2 e−dx (e x1)3 e− dy =0 6 ¡ y −yx2 ¢ dy dx =(y 1)2 7 dy dx =sinx ¡ cos2y −cos2 y ¢ 8 x p 1−y2 dx = dy 9 (e xe−) dy dx = y2 (21) ds dr = ks, 1 s ds = kdr, Z 1 s ds = k Z dr, lns = krc 1, s = ekrc 1 s = ekrec 1 = c 2ekr, (c 2 = ec 1), s = ±c 2ekr, s = cekr, (c = ±c 2) (22) dp dt = p−p2, 1Given that dy/dx = ye^x such that x = 0, y = e The value of y(y > 0) when x = 1 will be asked in Differential equations by Sarita01 ( 535k points)
*Thanks for the A* First off, notice that this differential equation is of the form , and notice that this differential equation, in current form, is not exact We can verify this byQuestion Solve The IVP (e^x y)dx (2xye^y)dy = 0, Y(0) = 1 Detailed Steps And Explanation Very Much Appreciated Detailed Steps And Explanation Very3ex tan y dx (1 – ex) sec2y dy = 0 The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is therefore, its order is 2 Since the given differential equation is not a polynomial in therefore, its degree is not defined



Find The General Solution To 2 Ye Xy Dx Xe Xy Chegg Com



How To Solve Show The Differential Equations Are Exact 2xy Y Tany Dx X 2 X Tany 2 Secy 2 2 Dy 0 Te Tx 2x Dx Dt Xe Xt 0 Quora
Ex 95, 10 In each of the Exercise 1 to 10 , show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve each of them (1𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) (1−𝑥/𝑦)𝑑𝑦=0 Since the equation is in the form 𝑥/𝑦 , we will take 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 Instead of 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 Step 1 Find 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 (1𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) (1−𝑥/𝑦Originally Answered How can I solve (e^(xy) ye^y) dx (xe^(y) 1) dy=0? e^xtan y dx (1 e^x)sec^2y dy = 0 12th Maths Differential Equations Solving Differential Equations Variable Separable Method e^xtan y dx (1 e^x)sec^



Solve Xy Cos Xy Sin Xy Dx X 2cos Xy Dy 0 Youtube




First Order Differential Equations Ppt Download
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Solve the differential equation x(1 y^2)dx y(1 x^2)dy = 0 Join / Login maths Solve the differential equation x Ex 94, 10 For each of the differential equations in Exercises 1 to 10, find the general solution 𝑒^𝑥 tan〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥(1−𝑒^𝑥 ) sec^2〖𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0〗 〗 𝑒^𝑥 tan〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥(1−𝑒^𝑥 ) sec^2〖𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0〗 〗 𝑒^𝑥 tan〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥=−(1−𝑒^𝑥 ) sec^2〖𝑦 𝑑𝑦〗 〗 𝑒^𝑥 tan〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗=(𝑒2xydxx2dy=0 Three solutions were found d = 0 y = 0 x = 0 Step by step solution Step 1 Equation at the end of step 1 3x2yd = 0 Step 2 Solving a Single Variable Equation What is the solution of the differential equation ydx (xx^2y)dy=0



Which Of The Following Ordinary Differential Chegg Com




Solve The Differential Equation Y E X Y Dx X E X Y Y 2 Dy Y
Find the particular solution of the differential equation xdy/dx y x cosec (y/x) = 0;Simple and best practice solution for (x^2xyy^2)dx(xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it Show that y = e^x (A cosx B sinx) is a solution of the differential equation d^2 y/dx^2 2(dy/dx) 2y = 0) asked May 10 in Differential Equations by Yajna ( 299k points) differential equations




Misc 18 General Solution Ex Dy Y Ex 2x Dx 0 Miscellaneous



What Is The Solution Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx 1 E X Y Quora
y = 1/2e^(x^2) c This is a First Order Separable DE, so we can just separate the variable in it's current form to give;Find dy/dx y^2=1/(1x^2) Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set asThis is a tutorial about Exact Differential Equation of (x2y)dx 2(yx)dy=0Note we set (x2y) as our M and 2(yx)




Differential Equations Solved Examples 17
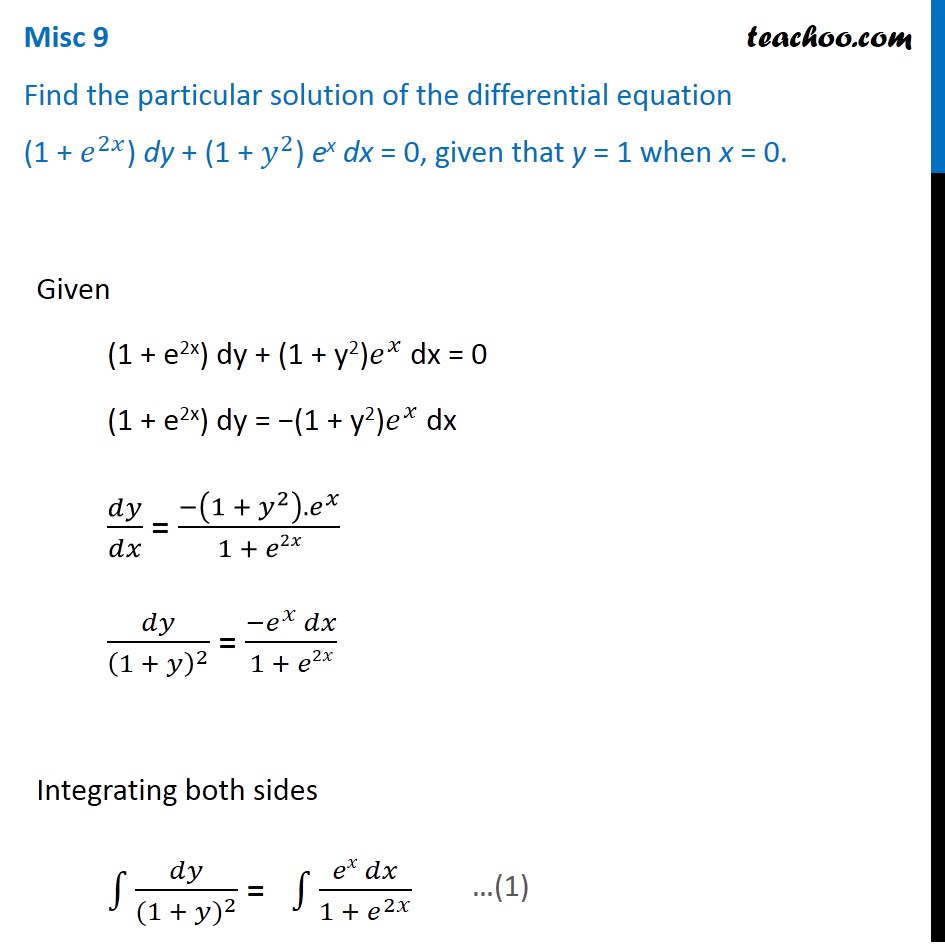



Misc 9 Find Particular Solution 1 E2x Dy 1 Y2 Ex
*Thanks for the A* First off, notice that this differential equation is of the form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0, and notice that this differential equation, in current form, is not exactThis is short video, Math Escape! y = ln ( 1/(e^x C) ) dy/dxe^(xy)=0 this is separable dy/dx= e^(xy) dy/dx= e^x e^y e^(y) dy/dx= e^x int\ e^(y) dy/dx \ dx=int e^x \ dx int\ e^(y) \ dy
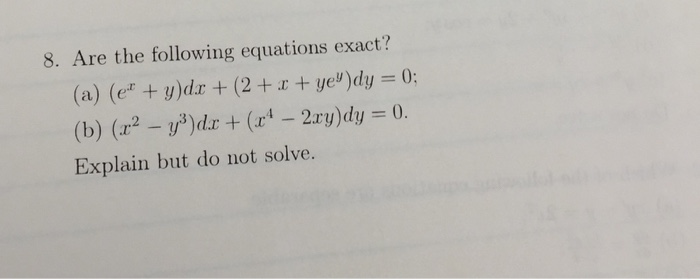



Are The Following Equations Exact E X Y Dx 2 Chegg Com




Ex 9 5 10 Show Homogeneous 1 Ex Y Dx E X Y 1 X Y
Answer to Solve the initial value problems (2xye^x^2y 1/y^2) dx (x^2 e^x^2y 2x/y^3 ye^y)dy = 0, y(0) = 2 y^2dx (xySolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreGiven that y = 0, when x = 1 asked in Mathematics by monuk ( 680k points) differential equations




Ma22s6 Homework 5 Solutions ˆ Question 1



What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora
Solve the following differential equation (1 ex/y)dx ex/y(1 x/y)dy = 0 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesThe equation ydx (2x ye^y)dy =0 can be written in normal form for the unknown x(y) as dx/dy 2x/y = e^y The integrating factor is y^2 and the solution is x(y) = (1/y^2)Integral of (y^2)(e^y)dy CIntegrating by parts obtain x(y) = (1/y^2The ODE is homogeneous ODE of order one This is because the coefficients of dx and dy are both homogeneous two variables functions of the same order I suggest you write the ODE as y′ = 32t2t2−t−2 = f (t), (x = 0,t = y/x) Find the solution of (xy^22x^2y^3)dx (x^2yx^3y^2)dy=0




Solve The Given Differential Equation By Using An Chegg Com




1 First Order Ode S 18 03 Exercises 1a Introduction Separation Of Variables
Int dy = int xe^(x^2) dx And note we can rewrite as int dy = 1/2int 2xe^(x^2) dx So we can integrate to give y = 1/2e^(x^2) c Example 17 Show that the differential equation 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦=0 is homogeneous and find its particular solution , given that, 𝑥=0 when 𝑦=1 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦 = 0 Step 1 Find 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑦 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) 𝑑𝑥(𝑦−2𝑥𝑒^(𝑥/𝑦) )𝑑𝑦=0 2𝑦𝑒^(𝑥Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Solution of the differential equation y(2xy e^x) dx e^x dy = 0 is



Www Math Tamu Edu Srlee Math308 Hw 3 Sol Pdf
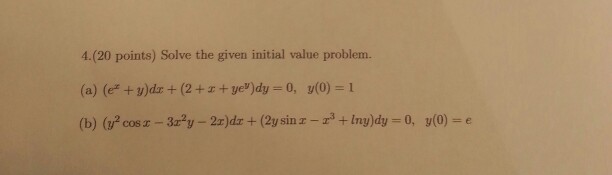



Solve The Given Initial Value Problem E X Y Dx Chegg Com
(b) 2 x y dx ( y 2 x 2) dy = 0 Here, M = 2 x y, M y = 2x, N = y 2 x 2, and N x = 2 xNow, ( N x M y) / M = ( 2 x 2 x ) / ( 2 x y) = 2 / yThus, μ = exp ( ∫ 2 dy / y ) = y2 is an integrating factor The transformed equation is ( 2 x / y ) dx ( 1 x 2 y2) dy = 0 Let m = 2 x / y, and n = 1 x 2 y2Then, m y = 2 x y2 = n x, and the new differential equation is exactSolved Solve (e^ (x)y)dx (2xye^ (y))dy=0 Subject To Y (0)=1 Cheggcom math other math other math questions and answersFactor out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), 'd 2 x 2 y 3 ' d 2 x 2 y 3 (1y x) = 0 Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'd 2 x 2 y 3 ' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying d 2 x 2 y 3 = 0 Solving d 2 x 2 y 3 = 0 Move all terms containing d to the left, all other terms to the right Simplifying d 2 x 2 y 3 = 0 The solution to this equation




X Y Dx Dy 0 Novocom Top




Solutions To Problems In Chapter One Mathematics
Given x dxye−x dy= 0, y(0) = 1 x d x y e − x d y = 0, y ( 0) = 1 We can write it as xdx = ye−xdy x d x = y e − x d y We will change this to the variable separable form f(x)dx =g(y y^2 = x^2(2lnx c) We can rewrite this Ordinary Differential Equation in differential form (x^2 y^2) \ dx xy \ dy = 0 A as follows \ \ \ \ dy/dx = (x^2 y^2)/(xy) dy/dx = x/y y/x B Leading to a suggestion of a substitution of the form u = y/x iff y = ux And differentiating wrt x whilst applying the product rule dy/dx = u x(du)/dx Substituting into the Libro Ecuaciones diferenciales de Dennis G ZillEcuacion diferencial de primer orden
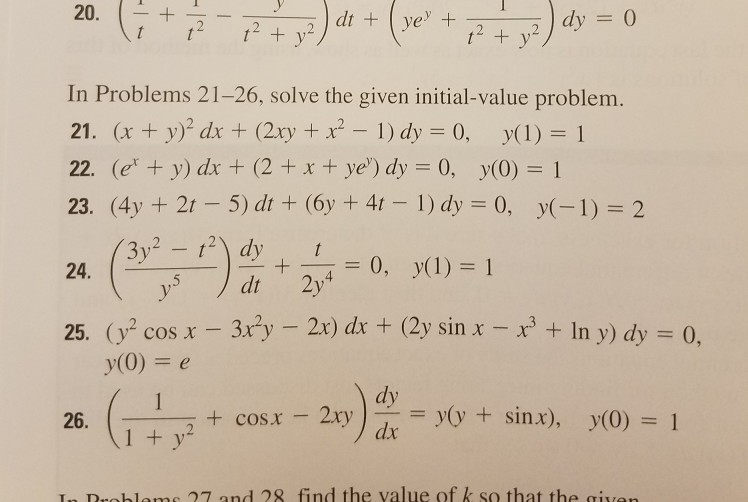



In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com




Dy Dx 2xy F X Y 0 2 Novocom Top
Simple and best practice solution for (x^2)dxy(x1)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW The solution of the differential equation, `e^x(x 1)dx (ye^y xe^x)dy = 0` wi(x2y2)dx=2xydy Geometric figure Two Straight Lines Slope = 1 xintercept = 0/1 = yintercept = 0/1 = Slope = 00/00 = 1000 xintercept = 0
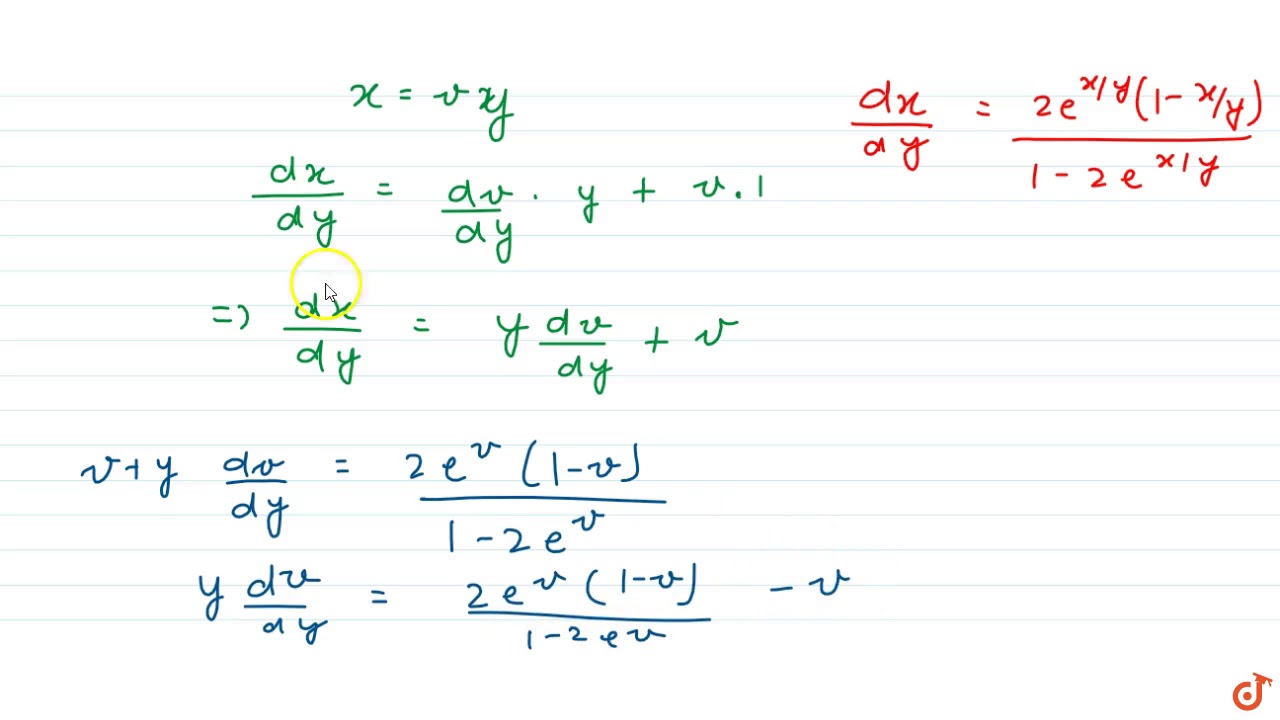



1 2e X Y Dx 2e X Y 1 X Y Dy 0 Youtube



Solve The Following Differential Equation E Xy Dy Dx Chegg Com
Solve the differential equation 3e^x tan y dx (2 e^x)sec^2 y dy = 0, given that when x = 0, y = pi/4 asked in Mathematics by Samantha (*Thanks for the A* First off, notice that this differential equation is of the form mathM(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0/math, and notice that this differential equation, in current form, is not exact We can verify this by taking the mixed partial deriv 1 1 y dy dx = x2 ∫ 1 1 y dy dx dx = ∫ x2 dx ∫ 1 1 y dy = ∫ x2 dx ln(1 y) = x3 3 C 1 y = ex3 3 C = ex3 3 eC = Cex3 3 y = Cex3 3 −1 Applying the IV 3 = Ce0 −1 = C −1 ⇒ C = 4 y = 4ex3 3 −1




First Order Differential Equations Ppt Download




Y 2xy E X Dx E Xdy 0 Novocom Top




Find The General Solution Of The Following Chegg Com




X Y Dx Dy 0 Novocom Top




E X Y Dx E Y X Dy 0 Youtube




First Order Differential Equations Ppt Download



E X Y Ye Y Dx Xe Y 1 Dy Y 0 0 Y 1 Chegg Com




The Solution Of The Differential Equation E X X 1 Dx Ye Y X



Http People Math Umass Edu Wchen M331 Midterm Sol Pdf




How To Solve Show The Differential Equations Are Exact 2xy Y Tany Dx X 2 X Tany 2 Secy 2 2 Dy 0 Te Tx 2x Dx Dt Xe Xt 0 Quora




In Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X Y 2 Chegg Com




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Exact Equations Example 1 Video Khan Academy



How To Solve This Exact Equation 2xe Y E X Dx X 2 1 E Y Dy 0 Quora



How To Solve Math E X Y Ye Y Dx Xe Y 1 Dy 0 Math Quora




Example 17 Show 2y E X Y Dx Y 2x Ex Y Dy 0 Particular



Search Q E 5e 1 Graph Tbm Isch




Y 2xy E X Dx E Xdy 0 Novocom Top




Chapter 04 2500 Solved Problems In Differential Equations Docsity
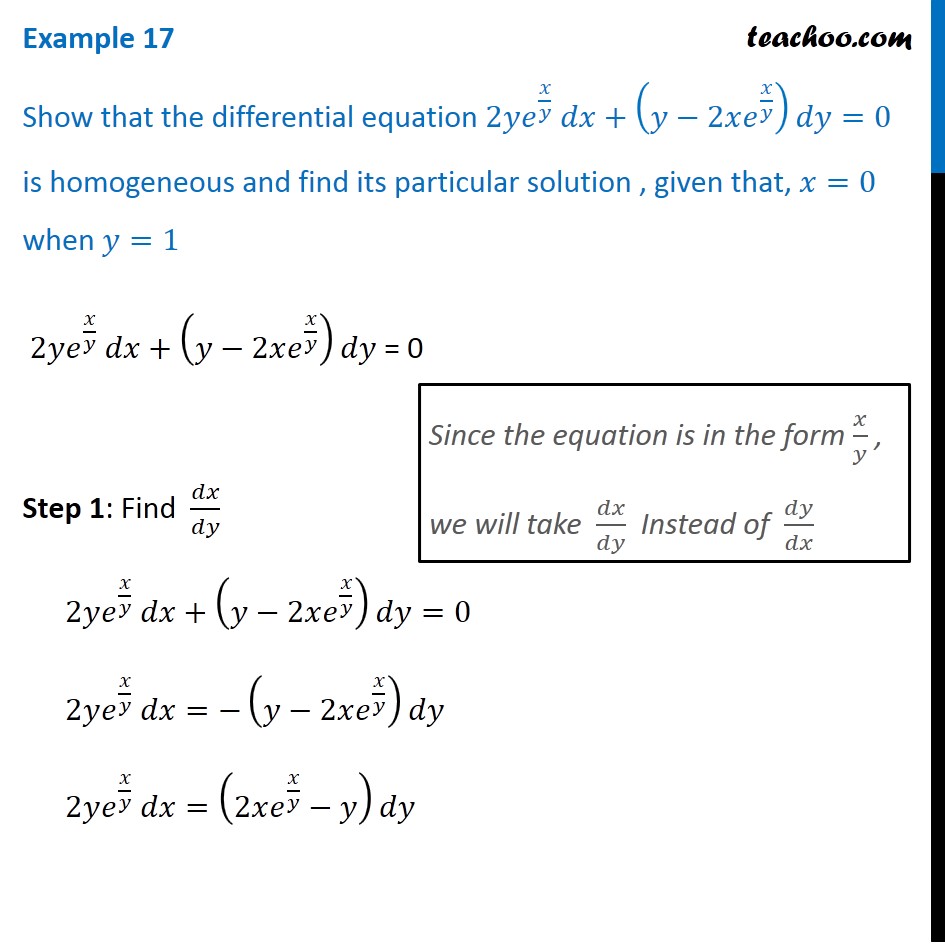



Example 17 Show 2y E X Y Dx Y 2x Ex Y Dy 0 Particular




Xexydxyexydy0 Ysqrt X2c1y Sqr See How To Solve It At Qanda



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf
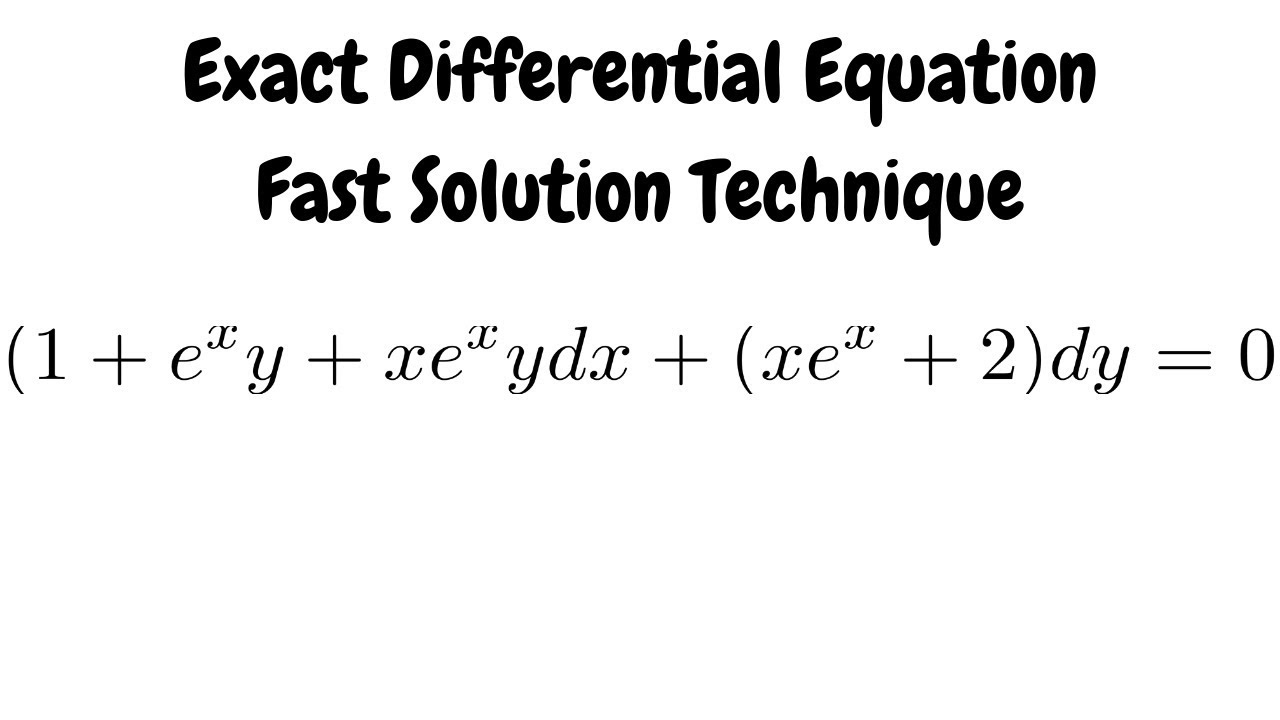



1 E Xy Xe Xy Dx Xe X 2 Dy 0 Exact Differential Equation Shorter Solution Youtube




Solve The Following Initial Value Problems E X Chegg Com



What Is The General Solution Of The Ydx Xy 2 X Y Dy 0 Quora
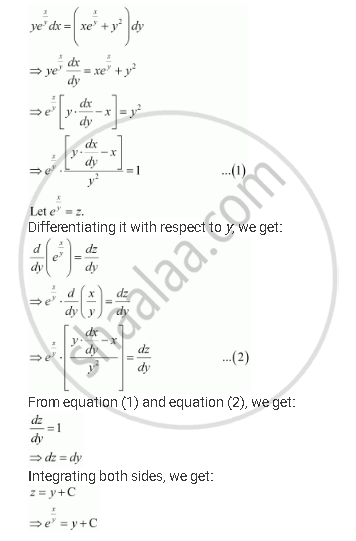



Solve The Differential Equation Ye X Y Dx Xe X Y Y 2 Dy Y 0 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




11 Y Ln Y E Xy Dx 1 Y X Ln Y Dy 0 Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander Estrada Youtube




E X Y Dy Dx E Y E 2x Y Youtube




Engineering Mathematics Notes




In Problems 1 26 Solve The Given Differential Chegg Com



Http Fractal Math Unr Edu Ejolson 285 15 Extraprob Pdf



How To Solve The Differential Equation X X Y Dy Y 2dx 0 Quora
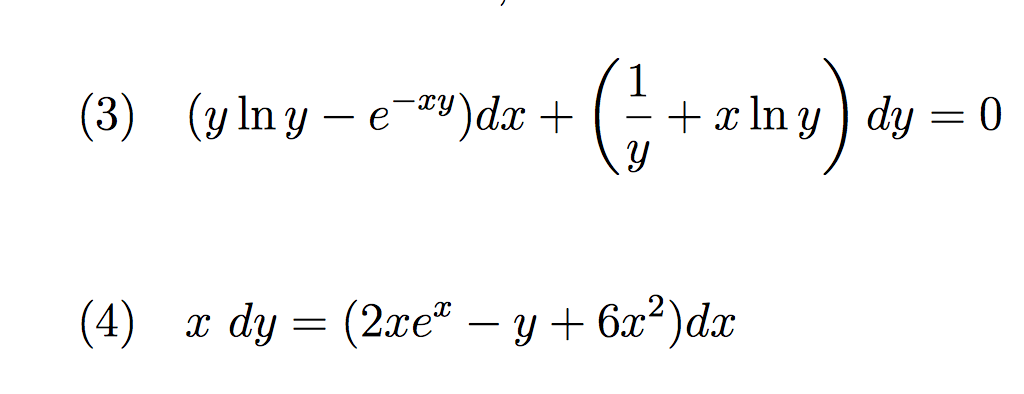



Determine Whether The Given Equation Is Exact If Chegg Com




Exact Differential Equations
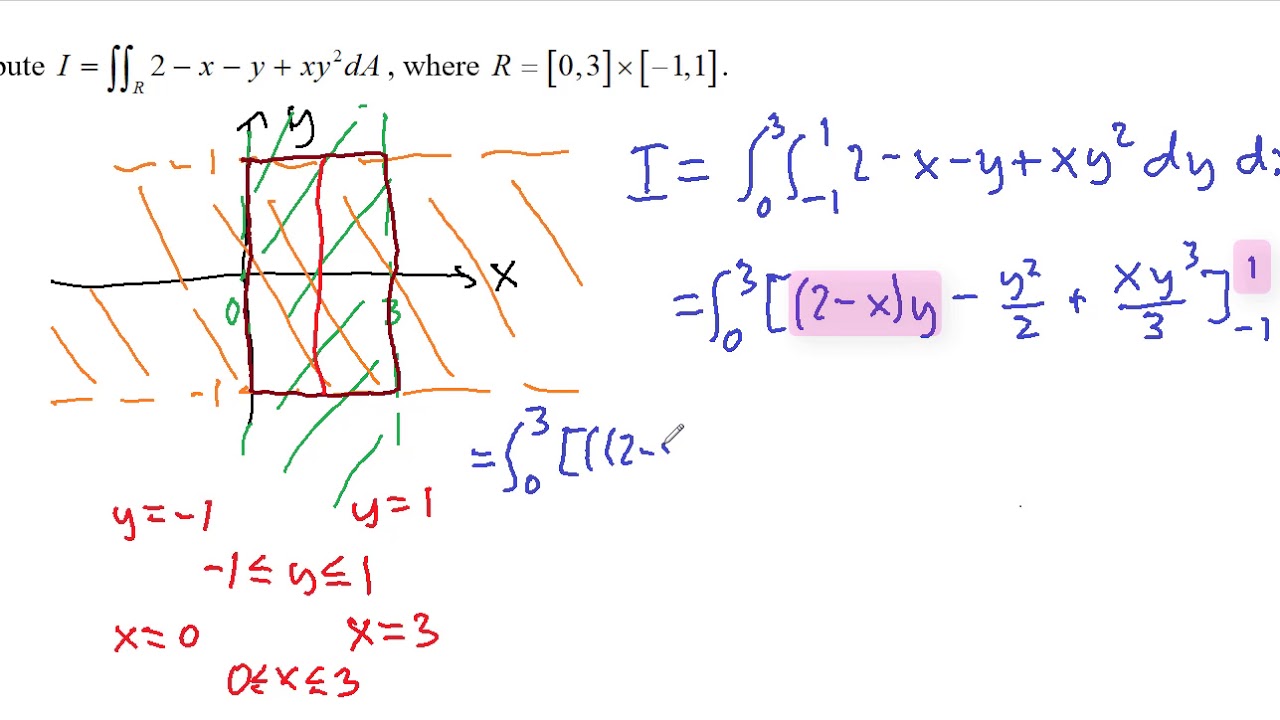



Double Integrals Volume And Average Value




Differential Equations Solved Examples 17



Solved Below Is A Write Whether The Differential Equations Given In Ordered Items Are Exact Differential Equations According To The Results You Fo Course Hero




Ex 9 5 10 Show Homogeneous 1 Ex Y Dx E X Y 1 X Y




Tutorial Ode 1718 Trims 2 Ordinary Differential Equation Rates
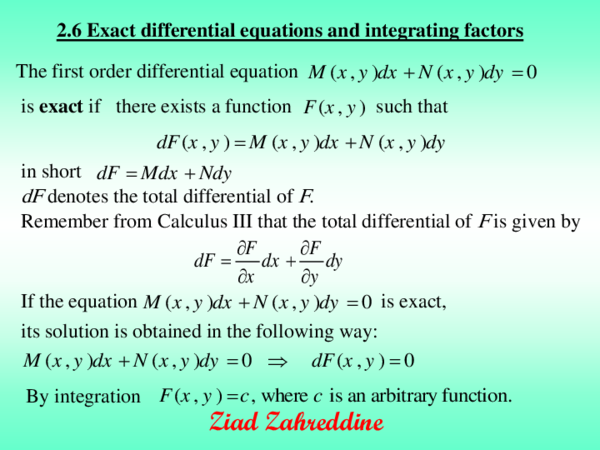



Pdf 2 6 Exact Differential Equations And Integrating Factors Mirna Mansour Academia Edu




The Solution Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx E X Y X 2e Y



How Do L Solve The Initial Value Problem X 2 Y 2 Dy Dx Xy Y 1 2 Quora




The Solution Of The Differential Equation E X X 1 Dx Ye Y Xe X Dy 0 With Initial Cond Youtube



Www Math Tamu Edu Irinaholmes M308f M308f Hw3 Sol Pdf



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
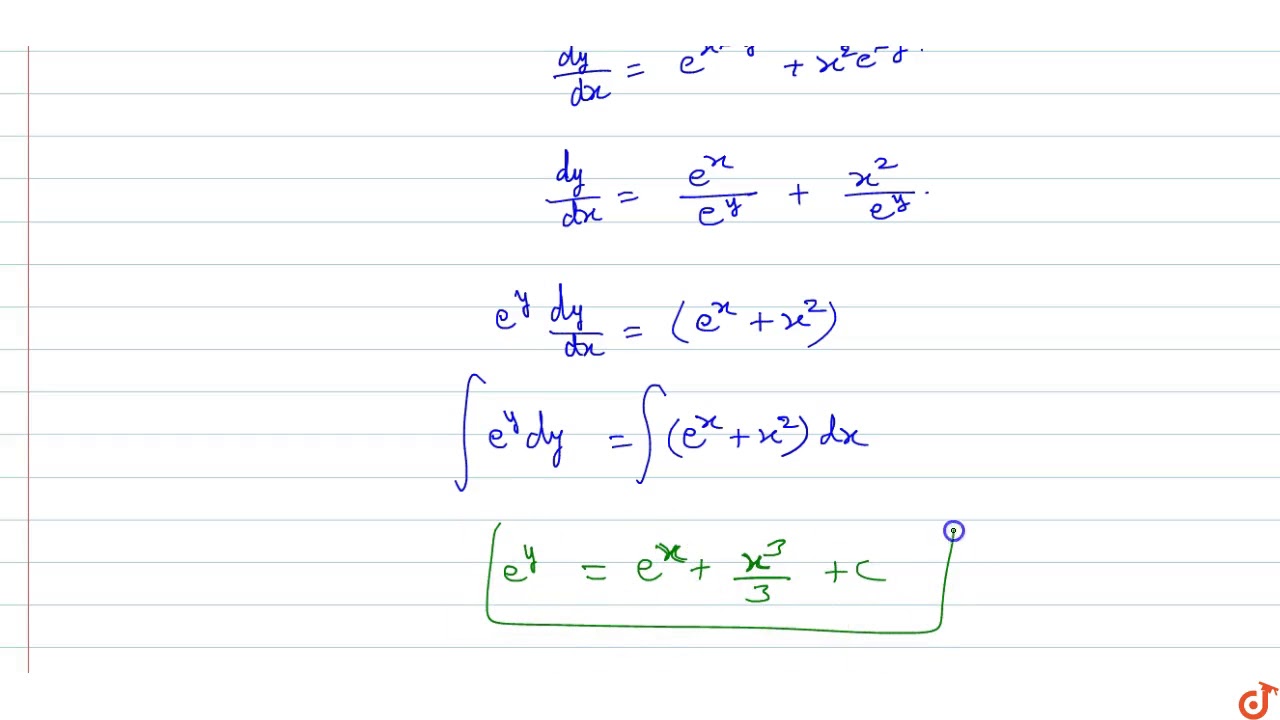



The Solution Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx E X Y X 2e Y Is Youtube



Find The Exact Coordinates Of The Centroid Where Y E X Y 0 X 0 X 3 Mathskey Com




Q 3 Find The Integrating Factor And Solve The Exact Solution Consider The Differential Equation E X Y Cosy Cosx 2e 2x Y Dx Sinx E X Y Siny 3y 2e Y Dy Q 5 Prove Socratic




Misc 10 Solve Y Ex Y Dx Ex Y Y2 Dy Chapter 9 Class 12




Find Particular Solution Of Y E Y Dx Show That X Y Dy X 2y



Q Tbn And9gcq69xqaiwgxy95 44f5sqsm2pnlgxvor Roue6xadfczqpkv4qx Usqp Cau




Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 E X Y Dx E X Y 1 X



The Solution Of Y 2x 2y E X Dx E X Y 3 Dy 0 If Y 0 1 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How To Solve 2x Tany Dx Sec Y Sec Y Dy 0 With Separable Ode Quora



How To Solve The Differential Equation Xy Dx X 2 2y 2 Dy 0 Quora




1 First Order Ode S 18 03 Exercises



Differential Equations



Ordinary Differential Equations




How Accurately Can You 1 Predict Y From



Www Cfm Brown Edu People Dobrush Am33 F17 Hw S3 Pdf




Find Particular Solution Of Y E Y Dx Show That X Y Dy X 2y
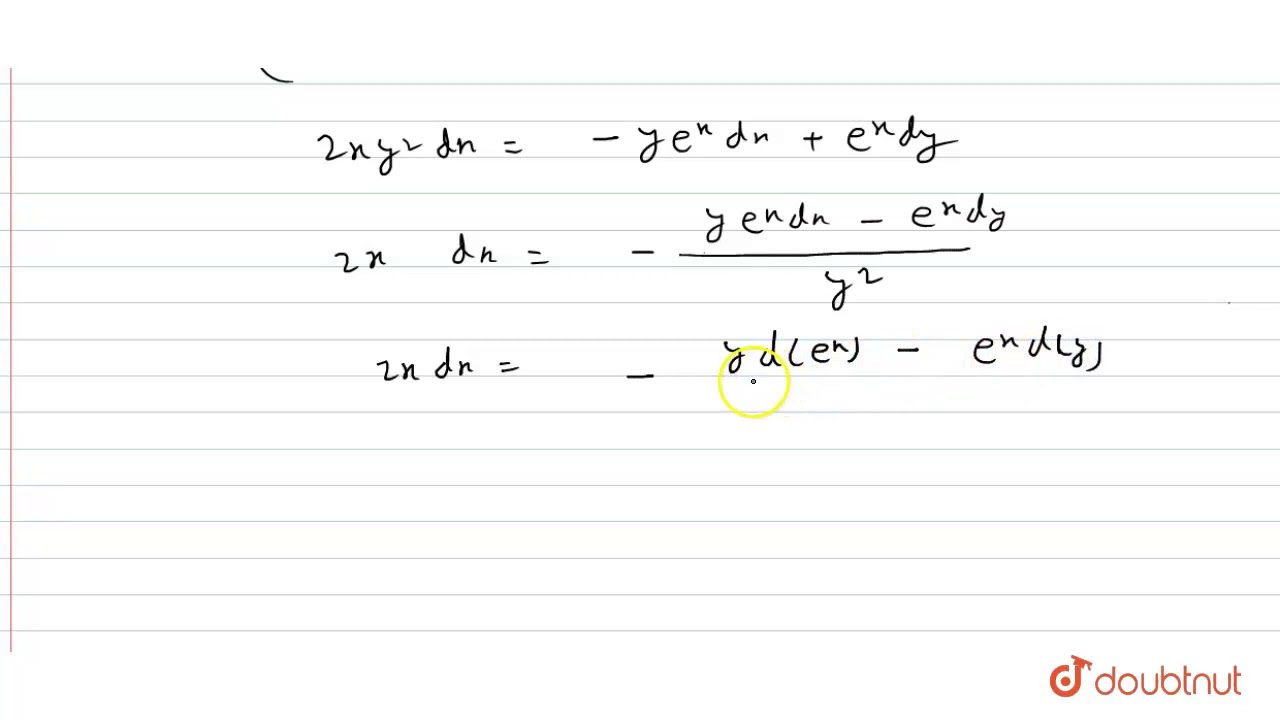



The Solution Of Y 2xy E X Dx E Xdy 0 Is A X 2 Ye X C B Xy 2 E X C C Youtube



Homogeneous Differential Equation




Math 432 Hw 2 4 Solutions




Answered 15 Which Of The Following Is The Bartleby
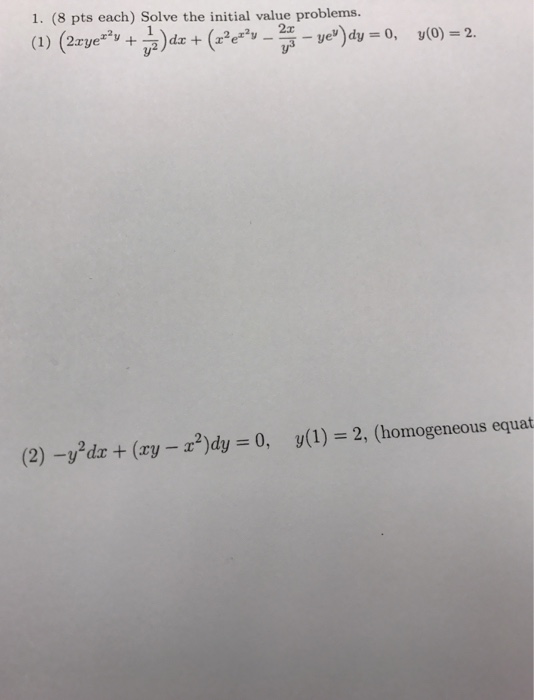



Solve The Initial Value Problems 2xye X 2y Chegg Com
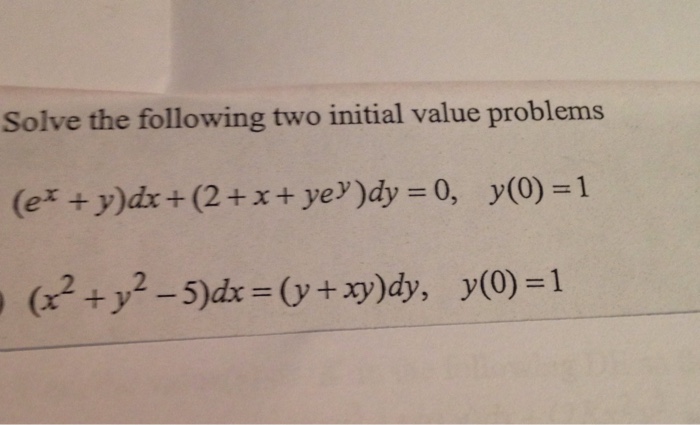



Solve The Following Two Initial Value Problems E X Chegg Com
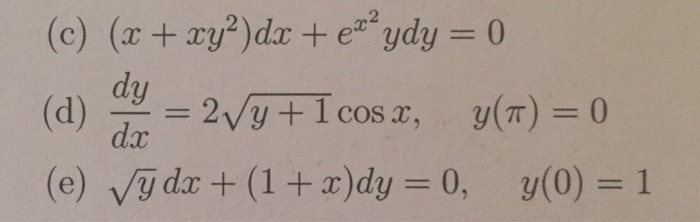



X Xy 2 Dx E X 2 Ydy 0 Dy Dx 2 Sqrt Y 1 Chegg Com




Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 E X Y Dx E X Y 1 X




X Dy Dx Y E X X 0 E Xdy Dx 2e Xy 1 Xy Chegg Com
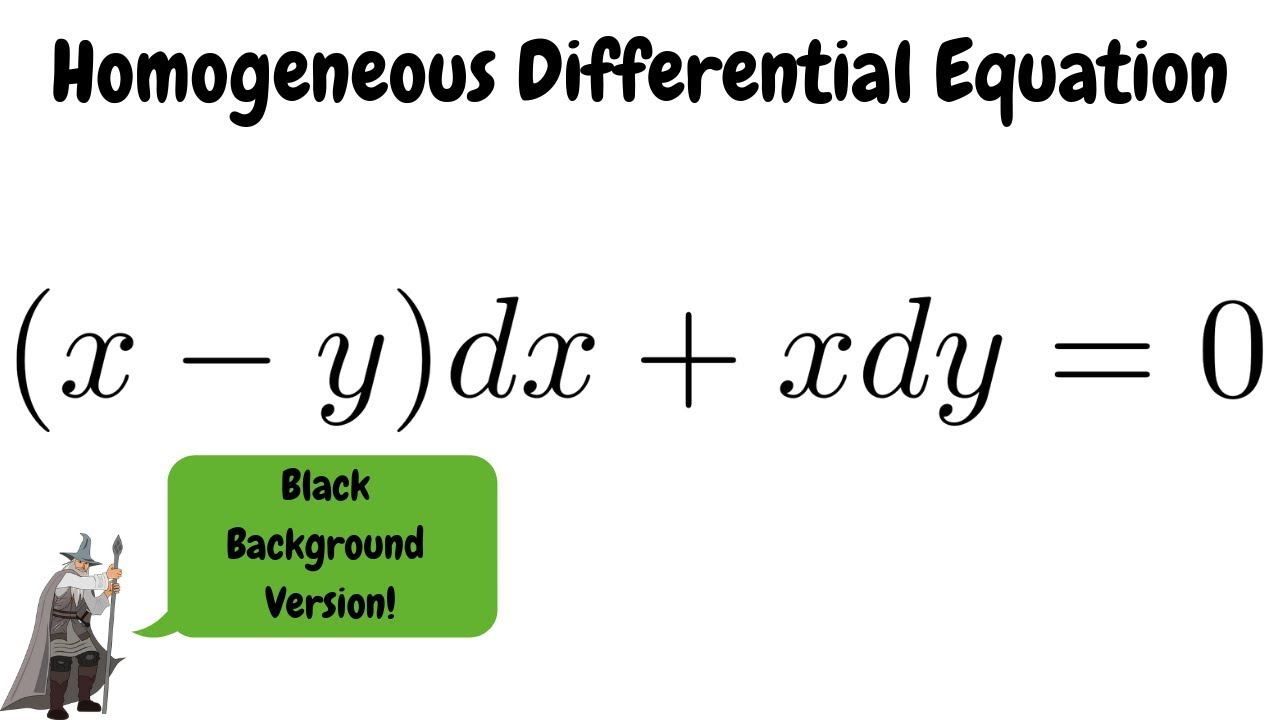



Homogeneous Differential Equation X Y Dx Xdy 0 Youtube




Ye X Ydx Xe X Y Y 2 Dy Maths Questions




Y 2 E Xy 2 4x 3 Dx 2xye Xy 2 3y 2 Dy 0 Brainly In




Ex 9 5 10 Show Homogeneous 1 Ex Y Dx E X Y 1 X Y



Find The General Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y2 X Etan 1y Dy Dx 0 Studyrankersonline
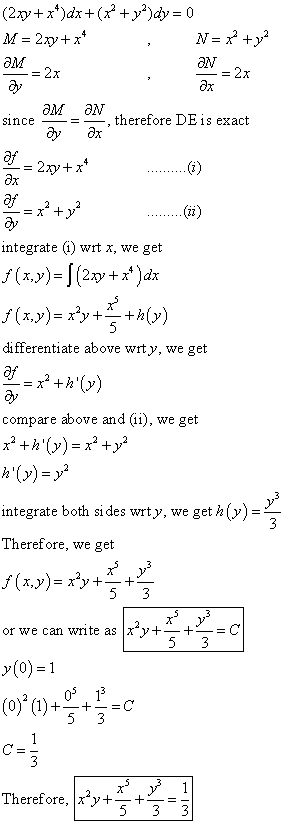



Differential Equations Solved Examples 17




Ex 9 6 11 Find General Solution Y Dx X Y2 Dy 0




Solving Separable Differential Equations Calculus Socratic




Math 432 Hw 2 4 Solutions Frostburg




What Is The Solution To This Ode 3x 2 4xy Y 2 Dx 2x 2 2xy 9 Dy 0 Quora



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿